Diamond Certificate
IGI vs GIA Diamond Certification
Did you know that once upon a time, transparency was described with phrases such as 'shiny as water', 'first water' and 'milky.' You had to take the word of the jeweller when they scratch-tested your diamond against other stones.
Just as no two people are the same, no two diamonds are identical — the unique facets and subtle variations in each stone create a beauty that is truly one of a kind. Gemological labs such as GIA (Gemological Institute of America) and IGI (International Gemological Institute)use a universal grading system to define a diamond’s appearance and officially grade its quality. A diamond’s grade is determined by the 4Cs: cut, color, clarity, and carat.
For diamonds sold online, it can be challenging to gauge their true value from a photograph alone, making it very important to check its grade to make sure you're making a fair and informed purchase. Knowing how to assess a diamond’s essential qualities ensures you select a piece that shines brilliantly as well as retains its value.
The most important of the 4Cs, cut refers to how a diamond’s facets interact with light. More than any other factor, cut determines the beauty of the stone. The more precise the diamond is cut, the more captivating it is to the eye.
Unlike shape (such as round or emerald) or facet style (like brilliant or step cut), the cut refers to the quality of workmanship. It determines how effectively the diamond reflects and refracts light to create that signature sparkle. Cut is the only one of the 4Cs that is affected by human expertise. Two diamonds might have the same clarity, colour and carat weight, but cut is what determines whether or not one is superior to the other. Simply put, cut is responsible for the quality and brilliance of a diamond’s sparkle.

A diamond’s cut is evaluated based on three key elements:
1. Precision: The relationship between the diamond’s size, angles and proportions across different parts of the stone.
2. Symmetry: The accuracy with which each facet is aligned and how cleanly they intersect.
3. Polish: The detailing, placements of the facets and the outside finish of the diamond.
The grading scale ranges from Excellent to Poor.
Color refers to the natural presence or lack of color visible within a diamond. Diamonds that appear slightly yellow or brown are considered to have more color, which reduces their color grade and value. Generally, the clearer and more colorless a diamond is, the higher its value.
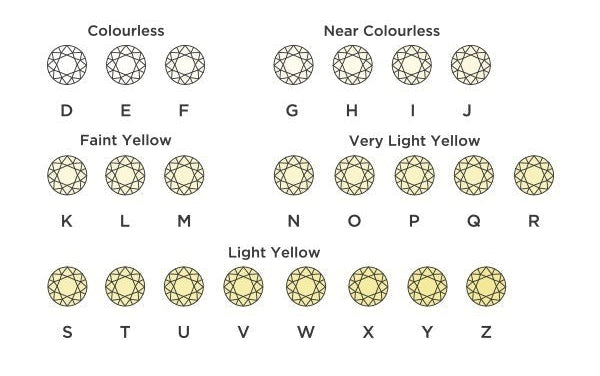
In a clear, colorless diamond, light passes through effortlessly, enhancing its brilliance. However, as color increases, light has a harder time passing through, often making the diamond appear darker or less vibrant.
Most diamonds fall within a spectrum ranging from completely colorless to those with a visible yellow or brown tint. The rarest and most expensive diamonds are graded D, E, or F, indicating they are colorless. This grading scale runs down to Z, where the presence of color becomes more noticeable. Diamonds that display color beyond Z, or appear in shades like pink, blue, or orange, are classified as Fancy Colored Diamonds.
While Mined Diamonds can be found across this entire scale, Lab Grown Diamonds are typically graded J (near colorless) or better. This is because, in the controlled environment of a Lab, the mineral contamination that cause color are far less likely to occur, resulting in clearer stones by default.
Clarity measures the purity of a diamond. During a diamond’s formation, it’s common for tiny impurities to become trapped either inside the diamond or on its surface.
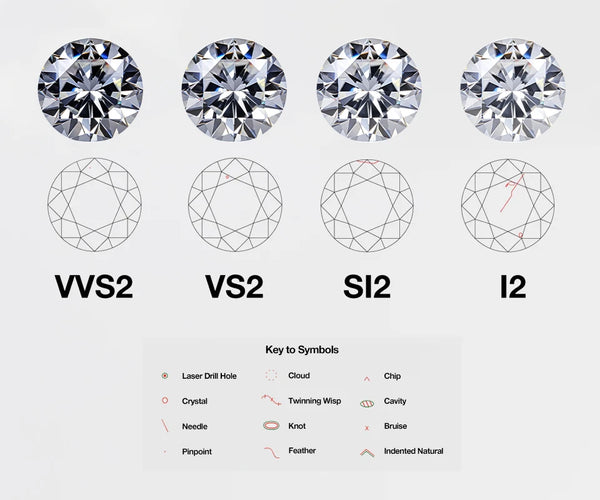
Clarity characteristics are divided into two types: Inclusions (internal features) and Blemishes (external marks). Even when these are too small to be seen without magnification, they can still affect how light moves through the diamond. As a result, their size, shape, and position play an important role in diamond grading. Importantly, Inclusions do not affect the structural stability of a diamond.
There are 11 clarity grades, ranging from FL (flawless internally and externally) to I (with significant inclusions and blemishes).
Make sure to check a diamond’s certificate before you make a purchase, as a diamond with fewer imperfections will come at a higher asking price. Imperfections also give each diamond its own unique character, and to many, these add to its beauty.
Carat is a measurement of weight, derived from the word "carob"; in ancient times, carob seeds were used as a reference for diamond weight.

One carat weighs 1/5 of a gram and is divided into 100 points, so a diamond weighing 1.05 ct. is referred to as "one carat and five points". Today, precise measurements are taken to the hundredth decimal place to ensure complete accuracy.
Diamond prices rise exponentially with carat weight. So, a 2-carat diamond of a given quality is always worth more than two 1-carat diamonds of the same quality. However, the carat weight by itself does not determine a diamond’s value. Two diamonds of equal carat weight may have very different values based on the other factors: all the 4Cs have an influence on each other in diamond grading.
Lab Grown Diamonds have opened a world of possibilities, offering the same brilliance, strength and beauty as mined diamonds but at a far more accessible price. Grown under conditions that replicate the earth’s natural processes, they share the exact same physical and chemical properties as their mined counterparts, differing only in their origin.
Like Mined Diamonds, Lucira Jewelry's Lab Grown Diamonds are graded by the 4Cs, giving you a trusted framework to understand a diamond's qualities. However, the 4Cs are simply a guide, not a rulebook. No two diamonds are alike, true beauty lies in what you personally connect with and that’s what makes it truly special.